This is an old revision of the document!
Basic
The Connection/Basic controls aren't “Basic” in the sense that they are simple, but rather that these settings control the most fundamental network configuration of the router and other more specialized Gargoyle features depend on these settings. For this reason, it is best to configure these options first and only change them when absolutely necessary.
Device Configuration

Gateway Configuration
The vast majority of the time you will want to select this option, and configure the router as a gateway. When this option is selected your local, LAN traffic is in a distinct subnet and protected from the WAN/internet with a firewall. This option must be selected in order to use firewall features including Quotas, QoS and Access Restrictions.
Wireless Bridge Configuration
When this option is selected, the router is put into a very specialized configuration in which the firewall is inactive, and the router connects via a wireless connection to another Access Point. It is possible to connect as a wireless client to another access point while in Gateway mode too, but what makes this configuration special is that the router and connected hosts will be in the same subnet as the upstream access point. Only activate this mode if you're sure you need it.
Internet / WAN
These controls specify how you connect to the internet. If these options are not set properly you will not be able to connect to anything outside your local network.
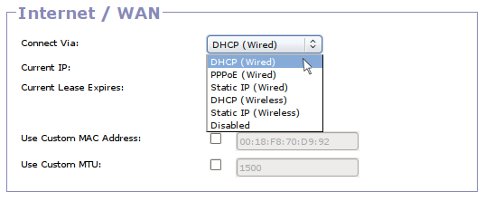
Connect Via
Select your connection protocol from this list. Most people will want to connect via the DHCP (wired) option, which is the default. If you have an ADSL connection you should select PPPoE, and put your ADSL modem in bridge mode. Below is a description of all connection options:
- DHCP (Wired): Obtain WAN IP dynamically with DHCP via the ethernet WAN Port.
- PPoE (Wired): Connect via PPPoE, which is suitable for ADSL connections. Your ADSL modem should be connected via an ethernet cable to the WAN port of the router.
- Static IP (Wired): Specify the WAN IP address, subnet mask and gateway manually, and connect via the ethernet WAN port.
- DHCP (Wireless): Connect to a wireless access point, and obtain an IP from it dynamically via DHCP. The WAN ethernet port will not be used.
- Static IP (Wireless): Connect to a wireless access point, and specify the WAN IP address, subnet mask and gateway manually. The WAN ethernet port will not be used.
- 3G (GSM): This option will only appear in the menu if you have a relatively modern router with (1) a USB port (2) 8+ MB of flash and 32+ MB of memory (3) Gargoyle 1.5.1+ (4) a 3G dongle currently attached to the router's USB port. This will allow you to configure a WAN connection via a 3G connection.
- Disabled: No WAN connection is configured, router will behave like a switch.
Custom MAC Address
Set a custom MAC (hardware) address for the WAN interface. Note that some router models do not support this feature. If your router doesn't support this feature, nothing bad will happen if you try to activate it, it just won't set the MAC as you requested.
Custom MTU
The Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) is the size of thelargest unit of data, in bytes, that is passed over the network. 1500, the default is usually a reasonable value, but if you are connecting via ADSL it is often a good idea to set this to 1470.
LAN
These settings control the Local Area Network (LAN), which consists of the router and the computers/devices that connect to it.
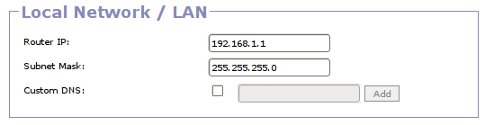
Router IP
This is the IP (IPv4) address of the router on the local network. 192.168.1.1 is the default. Router IP addresses should be in the 192.168.0.0/255.255.0.0, 172.16.0.0/255.240.0.0, or 10.0.0.0/255.0.0.0 subnets, which are reserved for local networks.
Subnet Mask
The LAN subnet mask. The default is 255.255.255.0. It doesn't make much sense to use a larger subnet mask, as a subnet mask of this size contains addreses for 254 hosts, far more than any router running gargoyle can handle by itself.
DNS Servers
These controls are slightly different depending on whether you have a router running the newer Gargoyle 1.5.X+ series of releases, or the older versions. However, in both cases, Gargoyle will, by default, serve DNS requests from your default ISP DNS servers.
In older Gargoyle releases you can enter the IP addresses of your preferred DNS servers if you do not widh to use ISP servers.
In newer Gargoyle releases, in addition to specifying custom DNS servers individually, you can specify that you want to use either the Google DNS servers, or those provided by OpenDNS.com from a dropdown box. This means that if you wish to use one of these alternate servers you will not need to enter the IP addresses manually. If you use the OpenDNS filtering service you should select the OpenDNS servers from this dropdown, and then configure your account in the Dynamic DNS section so that it gets updated properly. On newer releases that will allow the resolution of specialized top-level domains. While most people will not need this feature, leaving this checked does not inhibit performance, and will permit access to websites you otherwise would not be able to resolve.
Force Clients To Use Router DNS Servers
By checking this box you can force all clients connected to the router to use the DNS servers you specify above. Under normal circumstances clients can configure alternate DNS servers if they wish. However, if you check this option all DNS requests will be redirected to the specified servers. This is especially useful if you are using the OpenDNS filtering service.
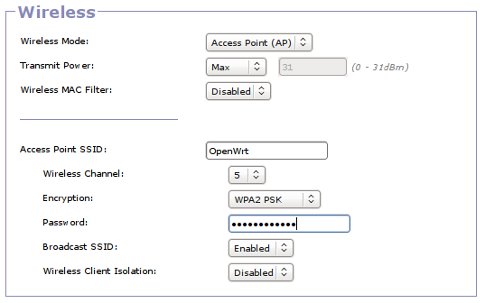
Wireless
These settings control the wireless capabilities of your router.